Feng: Difference between revisions
imported>Student221 |
imported>Student221 |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
[5] Roblyer, D., et al. "Objective detection and delineation of oral neoplasia using autofluorescence imaging", ''Cancer Prev. Res.'' '''2''', 423–431 (2009) | [5] Roblyer, D., et al. "Objective detection and delineation of oral neoplasia using autofluorescence imaging", ''Cancer Prev. Res.'' '''2''', 423–431 (2009) | ||
[6] Messadi, D. V., et al. "The clinical effectiveness of reflectance optical spectroscopy for the in vivo diagnosis of oral lesions", ''Int. J. Oral Sci.'' '''6''', 162–167 (2014) | |||
Revision as of 01:15, 14 December 2019
Introduction
Cancer screening is the procedure that aims to detect cancer before any signs or symptoms of cancer arise; it is potentially useful for medical diagnosis because early detection of cancer greatly increases the chances for successful treatment [1]. For the case of oral cancer, screening is particularly important as survival does correlate with stage, making early diagnosis and treatment optimal for this disease [2]. Unfortunately, the diagnosis constantly rely on physical examination followed by biopsy confirmation, which could result in delay in diagnosis [3]. As such, more and more research are being conducted to develop easy-to-use, cost effective oral cancer screening devices to encourage and improve this important procedure.
Background
Currently, there is a number of devices available on the market for oral cancer screening purpose. Some examples are Velscope®, ViziLite® and Identafi®. Extended studies on most of these devices are currently available in literature[4].
ViziLite is a disposable capsule like device that relies on chemiluminescence in 430-580 nm. Although researchers found its potential utility in identifying occult epithelial abnormalities, ViziLite suffers from high false positive and negative levels, and thus limiting its clinical application [4].
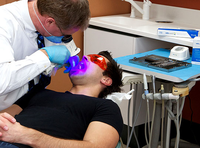
VELscope® is a hand held device that emits 400–460 nm wavelength light to excite auto-fluorescence from fluorophores in the mouth. Some researchers suggest that 405 nm wavelength light was able to discriminate neoplastic and non-neoplastic tissue with high sensitivity and specificity [5]. However, there has also been a number of criticisms on VELscope® for the limited capacity to extend its use in general dentistry. Researchers are still trying to improve its specificity to allow wider clinical use [4].
Identafi® is a probe like device designed for multi-spectral screening of oral disease. It emits three types of light: white, violet (405 nm) and green-amber (545 nm) light. The white light provides classical visual inspection and the violet light is for similar purpose as in VELscope®. The green-amber light, through reflection spectroscopy, is used to excites haemoglobin molecules in the blood, in order to visualise the vasculature [6].
Methods
Results
Conclusions
Appendix
You can write math equations as follows:
You can include images as follows (you will need to upload the image first using the toolbox on the left bar, using the "Upload file" link).
References
[1] https://www.who.int/cancer/detection/en/
[2] Ries LAG, Kosary CL, Hankey BF, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1973-1995. Bethesda, MD, NCI.2. American Cancer Society, Facts and Figures, 2000.
[3] https://oralcancerfoundation.org/discovery-diagnosis/cancer-screening-protocols/
[4] Mascitti, M., et al. "An Overview on Current Non-invasive Diagnostic Devices in Oral Oncology" Front. Physiol. 9, 1510 (2018)
[5] Roblyer, D., et al. "Objective detection and delineation of oral neoplasia using autofluorescence imaging", Cancer Prev. Res. 2, 423–431 (2009)
[6] Messadi, D. V., et al. "The clinical effectiveness of reflectance optical spectroscopy for the in vivo diagnosis of oral lesions", Int. J. Oral Sci. 6, 162–167 (2014)

