Rav: Difference between revisions
imported>Psych204B No edit summary |
imported>Psych204B No edit summary |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
60 IAPS pictures (images with affective content) were split into 30 pairs. Within a pair, one picture was designated as Picture 1 and the other as Picture 2. Picture 1 and Picture 2 were counterbalanced for valence and arousal (IAPS population ratings). In the fMRI, subjects were shown Picture 1 for 500ms followed by Picture 2 for 500ms. They were asked to make a choice between the two pictures. The chosen picture was displayed for 4s—a duration long enough to ensure that the preferred picture was viewed and processed; this attached real affective consequences to each choice. | 60 IAPS pictures (images with affective content) were split into 30 pairs. Within a pair, one picture was designated as Picture 1 and the other as Picture 2. Picture 1 and Picture 2 were counterbalanced for valence and arousal (IAPS population ratings). In the fMRI, subjects were shown Picture 1 for 500ms followed by Picture 2 for 500ms. They were asked to make a choice between the two pictures. The chosen picture was displayed for 4s—a duration long enough to ensure that the preferred picture was viewed and processed; this attached real affective consequences to each choice. | ||
Outside the fMRI, subjects were asked to rate each image on a 1-7 scale for valence and arousal | |||
== Hypothesis == | == Hypothesis == | ||
We | We expected to see 2 sets of results: | ||
1) Distinct areas of the brain would be active for high vs. low valence pictures and for high vs. low arousal pictures. Since a variety of | |||
= Methods = | = fMRI Methods = | ||
== Measuring retinotopic maps == | == Measuring retinotopic maps == | ||
Retinotopic maps were obtained in 5 subjects using Population Receptive Field mapping methods [http://white.stanford.edu/~brian/papers/mri/2007-Dumoulin-NI.pdf Dumoulin and Wandell (2008)]. These data were collected for another [http://www.journalofvision.org/9/8/768/ research project] in the Wandell lab. We re-analyzed the data for this project, as described below. | Retinotopic maps were obtained in 5 subjects using Population Receptive Field mapping methods [http://white.stanford.edu/~brian/papers/mri/2007-Dumoulin-NI.pdf Dumoulin and Wandell (2008)]. These data were collected for another [http://www.journalofvision.org/9/8/768/ research project] in the Wandell lab. We re-analyzed the data for this project, as described below. | ||
Revision as of 21:08, 11 March 2012
Back to Psych 204 Projects 2009
Affect and Choice: Background Information
Imagine deciding which of two equally priced and equally appropriate pictures to buy for a home office. Faced with such a decision, people are thought to consult their feelings and ask, “How do I feel about each option?” (Schwarz & Clore, 2003). A choice between the two affective states is thought to determine which picture is chosen.
Now imagine deciding whether to invest in risky high-yield stocks or safer lower-returning bonds. This decision involves considerations that are not purely affective. However, a growing literature suggests that even in such cases affective choice may play a pivotal role in decision making. Indeed, it has been suggested that affect serves as the “common currency” of decision making (Peters, Västfjäll, Gärling & Slovic, 2006). Decision makers decompose complex thoughts into affective states (Mellers, 2000; Pfister et al., 2008) that are then compared with each other, as in the picture example.
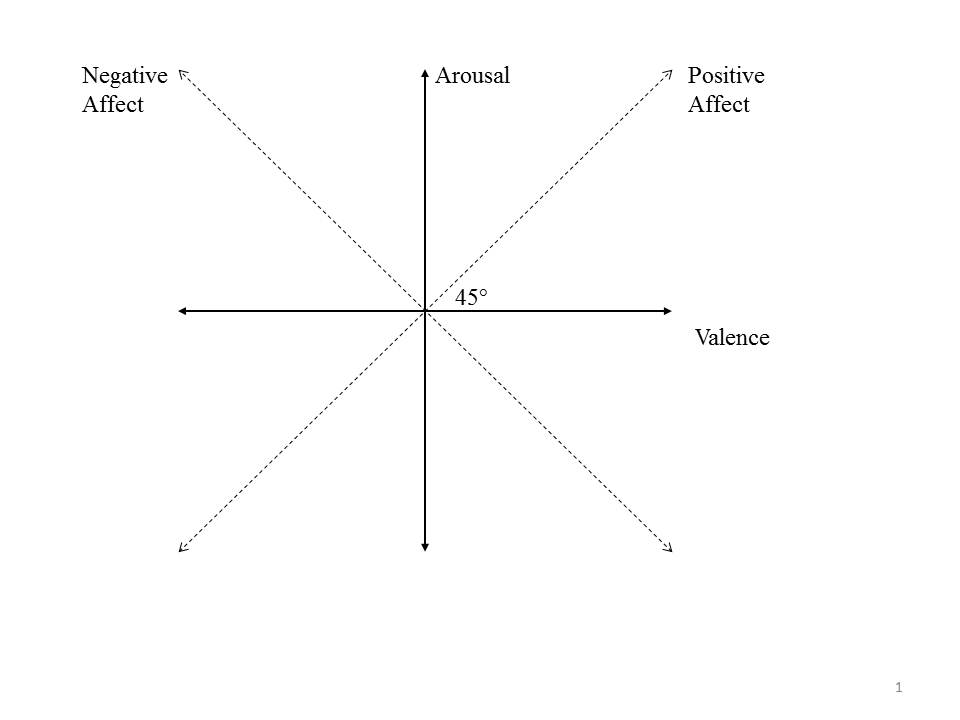
Despite the centrality of affective choice to decision making, it is not at all clear how choices between two affective states are made. Our starting point in addressing this issue is a distinction between two fundamental dimensions of affect—valence and arousal. The first, valence, represents the pleasantness/unpleasantness of the affect. The second, arousal, represents the degree of activation associated with the affect. These dimensions capture most of the variance in self-reported mood ratings (Osgood, Suci & Tanenbaum, 1957; Russell 1980; Barrett & Russell, 1999). In addition, cross cultural (Larsen & Diener, 1992), neurobiological (Posner et al., 2009), and developmental data (Russell & Bullock, 1985) demonstrate that – as Wundt (1912) postulated – valence and arousal are core components of affective states. Valence and arousal are often drawn as perpendicular dimensions to create an affective 2-space (Figure 1).
Experiment Structure
60 IAPS pictures (images with affective content) were split into 30 pairs. Within a pair, one picture was designated as Picture 1 and the other as Picture 2. Picture 1 and Picture 2 were counterbalanced for valence and arousal (IAPS population ratings). In the fMRI, subjects were shown Picture 1 for 500ms followed by Picture 2 for 500ms. They were asked to make a choice between the two pictures. The chosen picture was displayed for 4s—a duration long enough to ensure that the preferred picture was viewed and processed; this attached real affective consequences to each choice.
Outside the fMRI, subjects were asked to rate each image on a 1-7 scale for valence and arousal
Hypothesis
We expected to see 2 sets of results:
1) Distinct areas of the brain would be active for high vs. low valence pictures and for high vs. low arousal pictures. Since a variety of
fMRI Methods
Measuring retinotopic maps
Retinotopic maps were obtained in 5 subjects using Population Receptive Field mapping methods Dumoulin and Wandell (2008). These data were collected for another research project in the Wandell lab. We re-analyzed the data for this project, as described below.
Subjects
Subjects were 5 healthy volunteers.
MR acquisition
Data were obtained on a GE scanner. Et cetera.
MR Analysis
The MR data was analyzed using mrVista software tools.
Pre-processing
All data were slice-time corrected, motion corrected, and repeated scans were averaged together to create a single average scan for each subject. Et cetera.
PRF model fits
PRF models were fit with a 2-gaussian model.
MNI space
After a pRF model was solved for each subject, the model was trasnformed into MNI template space. This was done by first aligning the high resolution t1-weighted anatomical scan from each subject to an MNI template. Since the pRF model was coregistered to the t1-anatomical scan, the same alignment matrix could then be applied to the pRF model.
Once each pRF model was aligned to MNI space, 4 model parameters - x, y, sigma, and r^2 - were averaged across each of the 6 subjects in each voxel.
Et cetera.
Results - What you found
Retinotopic models in native space
Some text. Some analysis. Some figures.
Retinotopic models in individual subjects transformed into MNI space
Some text. Some analysis. Some figures.
Retinotopic models in group-averaged data on the MNI template brain
Some text. Some analysis. Some figures. Maybe some equations.
Equations
If you want to use equations, you can use the same formats that are use on wikipedia.
See wikimedia help on formulas for help.
This example of equation use is copied and pasted from wikipedia's article on the DFT.
The sequence of N complex numbers x0, ..., xN−1 is transformed into the sequence of N complex numbers X0, ..., XN−1 by the DFT according to the formula:
where i is the imaginary unit and is a primitive N'th root of unity. (This expression can also be written in terms of a DFT matrix; when scaled appropriately it becomes a unitary matrix and the Xk can thus be viewed as coefficients of x in an orthonormal basis.)
The transform is sometimes denoted by the symbol , as in or or .
The inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) is given by
Retinotopic models in group-averaged data projected back into native space
Some text. Some analysis. Some figures.
Conclusions
Here is where you say what your results mean.
References
Software
Appendix I - Code and Data
Code
Data
Appendix II - Work partition (if a group project)
Brian and Bob gave the lectures. Jon mucked around on the wiki.






