Stephanie
Background
LKcj Jaskdkghfls kjhkjcvx,mvkjifdjvjkrngkjv
To add an image, simply put text like this inside double brackets 'MyFile.jpg | My figure caption'. When you save this text and click on the link, the wiki will ask you for the figure.
lKSJ Dkdjfdsklj lkfj cvlkxcvlkjes;lfjewlkj
Heading1
KJS Cj fijlckxzcjioe.lkcmxzicj
Materials and Methods
Subjects
Subjects were 19 healthy, right-handed volunteers.
Memory Task
Subjects completed 12 scanned runs consisting of an encoding phase and a recognition test phase (see Fig. 1). Each encoding phase lasted 4.5 minutes, and the test phase lasted 1.5 minutes; separating the encoding and test phases was a delay period during which subjects performed an odd/even judgment task as a baseline condition.
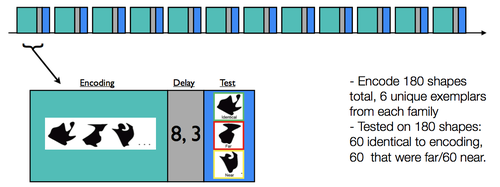
During a given encoding phase, subjects were presented with 15 unique shapes. Each of the 15 shapes was presented three times for 2.5 s each time (separated by a 1.5s ISI, during which a fixation was presented). Subjects were tasked with making a size judgment (i.e., aspect ratio; taller than wide, or wider than tall) for every shape.
For each test phase, subjects were presented with 15 shapes (2.5 s duration, 1.5 s fixation); critically, five of the shapes were identical to the studied shapes, five were perceptually near shapes ("near"), and five were perceptually far ("far"). These shape stimuli were designed [XXXXXXXXXXX]. For each of the 15 shapes, subjects were asked to rate if the shape was new or old, using a 1-5 confidence rating scale (1:sure new, 2:moderately sure new, 3:guess, 4:moderately sure old, 5:sure old).
Behavioral Analysis
XXXXkdaldkjsalkdjas ;lkjsalkdjaslkdjaslk cjaslkfjaslkd jsalkdj alskdj alksdj alksdj aldkj aslkdj acmxkcjuifqw;l
fMRI Analysis
MR acquisition
Imaging data were acquired on a 3.0 T Signa whole-body MRI system with a custom-built head coil (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI, USA).
In total, 2,400 functional volumes were acquired for each participant using a T2*-sensitive gradient echo spiral in/our pulse sequence (Glover and Law, 2001). Functional imaging parameters were optimized to provide whole brain coverage (TR=2000ms; TE= 30ms; flip angle = 75°; FOV = 22 cm; 3.44 x 3.44 x 4 mm resolution, 30 slices).
fMRI Analysis
The fMRI data was analyzed using Lyman, Nipype, Freesurfer, AFNI, and FSL software tools.
Pre-processing
All data went through a standard preprocessing pipeline using Freesurfer and FSL, including motion (RapidART) and slice time correction, realignment (middle volume of each run), skull stripping, temporal filtering (high-pass cutoff 128 Hz), and surface-based coregistration (bbregister). Data were spatially smoothed (6 fwhm, SUSAN -- only averages a given voxel with local voxels that have a similar intensity), scaled grand median of timeseries to 10000, & normalized for group analyses (nonlinear warp to FSL’s MNI152 space). Data were modeled using a double gamma function, and the first 5 frames of each run were discarded.
Results
Behavioral Results
First, kljskdjf s;lkjsdflk kdjsf ksdfjklsdjf kjl
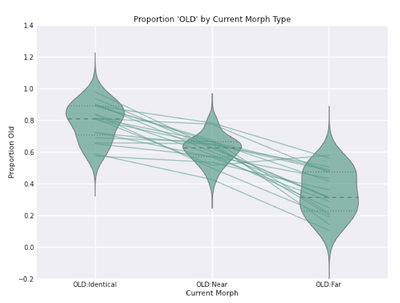
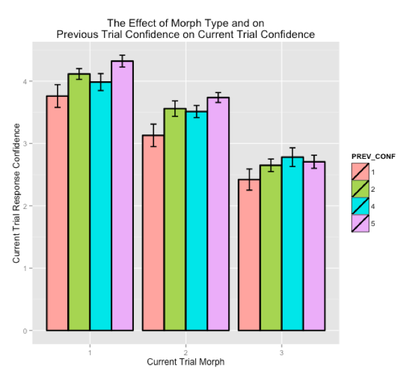
Then, skldjf klfjsdkfsjkcjxv;lcxkjvd dprimes...

K Jlkdsjfdslkfjsdlkfjds kjsdf lkasdjf;alsdkfj alsdkfj lskdjf
fMRI Results
KKLJkldjf skfjsdklfj kfj dsf;ls
Coding Regressors
Highpass Filter Cutoff
Conclusions
In summary, k jfklasjfdskaljd lksajdlksa jlksd
References
Software